Burns surgery in pediatrics focuses on treating burns in children, which can be particularly challenging due to their delicate skin and vulnerable anatomy. Pediatric burn surgeons use specialized techniques and equipment to manage burns, ensuring minimal scarring and optimal functional outcomes. Treatment may involve debridement, wound dressing, and skin grafting to promote healing and reduce the risk of infection. In severe cases, reconstructive surgery may be necessary to repair damaged tissue and restore function. Pediatric burn surgeons work closely with other specialists, such as pediatricians and plastic surgeons, to provide comprehensive care and support for children with burns. Burn surgery involves the acute treatment of burn injuries and the long-term reconstruction and rehabilitation. Key procedures include:
a. Acute Burn Care
Pediatric acute burn care involves providing immediate and comprehensive treatment to children who have suffered burns, typically within the first 24-48 hours after the injury. The goal of initial treatment is to prevent further tissue damage, reduce pain and discomfort, and promote healing. Burn wounds are cleaned and debrided to remove dead tissue, and topical antimicrobial agents are applied to prevent infection. Pain management is a critical aspect of pediatric burn care, as children may experience significant discomfort and anxiety. Medications such as lidocaine or ketamine can be used to manage pain, along with non-pharmacological interventions like comfort measures and emotional support. Fluid resuscitation is also essential to replace lost fluids and electrolytes, with intravenous fluids being the primary method of administration. Ongoing monitoring and assessment of the child's condition is crucial to ensure optimal recovery and minimize the risk of complications.
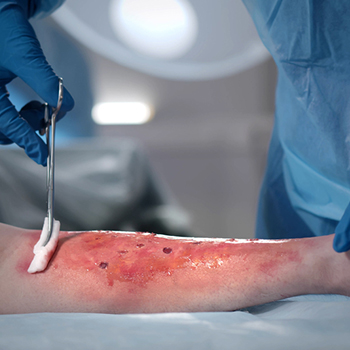
b. Post Burn Reconstructive surgeries
Pediatric post-burn reconstructive surgeries are a crucial aspect of burn care that aims to restore the appearance and function of burned areas in children. The goal is to promote optimal physical and emotional recovery, as well as minimize long-term psychological trauma. Common procedures include skin grafting, scar revision, and tissue expansion. Skin grafting involves transferring healthy skin from an unaffected area to cover burned areas, while scar revision aims to reduce or eliminate hypertrophic scars. Tissue expansion involves inserting an expander under the skin to stretch and expand the surrounding tissue, allowing for more natural-looking reconstruction. Pediatric burn patients often require multiple surgeries over several years to achieve optimal results. A multidisciplinary team of pediatric burn specialists, plastic surgeons, and physical therapists work together to address the complex physical and emotional needs of these children.


