Trauma and reconstructive surgery is a type of surgery that aims to repair or restore the physical function and appearance of tissues and organs damaged as a result of injury, disease, or birth defects. The goal of this type of surgery is to improve the patient's quality of life by restoring normal function, alleviating pain, and enhancing overall well-being. Trauma and reconstructive surgeons work to rebuild and repair damaged tissues, such as skin, bone, muscle, and nerve tissue, using a variety of techniques and materials, including skin grafts, prosthetics, and implants. The scope of trauma and reconstructive surgery is vast, encompassing procedures such as wound closure, facial reconstruction, hand surgery, and microsurgery. These procedures require great skill and attention to detail to ensure optimal outcomes and patient satisfaction. Trauma and reconstructive surgeons work closely with other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care for patients with complex injuries or conditions.
a. Open fractures
An open fracture, also known as a compound fracture, is a type of bone fracture where the broken bone pierces through the skin, often causing severe injury to surrounding soft tissue and potentially exposing bone and other internal structures. This type of fracture is considered a medical emergency and requires immediate attention. Open fractures are often caused by high-energy trauma, such as car accidents, falls from a height, or violent blows to the body. The severity of the injury can vary greatly, ranging from minor damage to life-threatening conditions. Treatment typically involves stabilization of the fracture, usually with internal or external fixation devices, as well as wound care to prevent infection. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to clean and stabilize the wound, repair damaged tissues, and restore bone alignment. Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent infection, promote healing, and minimize long-term complications.
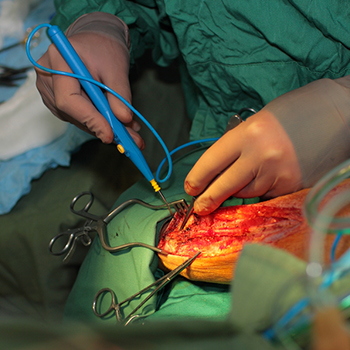
b. Limb salvage surgeries
Limb salvage surgery is a type of reconstructive surgery that aims to save a limb that has been severely injured or damaged due to trauma, infection, or disease. The goal of limb salvage surgery is to restore function and mobility to the affected limb, rather than amputating it. The procedure involves repairing or replacing damaged tissues, bones, and muscles to restore the limb's natural shape and function. This may involve reconstructing the skin, muscles, tendons, and bones, as well as reattaching severed nerves and vessels. Limb salvage surgery can be performed using various techniques, such as microsurgery, tissue transfer, and prosthetic reconstruction. The success of limb salvage surgery depends on the severity of the injury and the patient's overall health. While some patients may experience significant improvements in function and mobility, others may require ongoing rehabilitation and physical therapy to achieve optimal results.
c. Skin grafting
Skin grafting is a surgical procedure that involves transplanting healthy skin from one area of the body to another. This technique is often used to repair damaged or missing skin, such as after a burn or injury. The grafting process involves harvesting a layer of skin from the donor site, then attaching it to the recipient site using sutures, staples, or glue. The graft can be thin (split-thickness) or thick (full-thickness), depending on the area being treated. Skin grafting can help restore skin integrity, reduce scarring, and improve appearance. It is commonly used in reconstructive surgery, burns treatment, and aesthetic procedures like scar revision.
d. Local flap cover
Local flap coverage is a technique used in reconstructive surgery to cover defects or wounds on the skin. It involves creating a flap of healthy skin from nearby areas and relocating it to the affected area to cover the defect. The flap is typically designed to match the shape and color of the surrounding skin, allowing for a natural appearance. Local flaps can be used to repair small to medium-sized defects, and are often preferred over skin grafts because they have a lower risk of complications and better blood supply. They are commonly used to repair skin defects caused by trauma, surgery, or skin cancer.
e. Microvascular Free tissue transfer (free flaps)
Free flaps are a type of reconstructive surgery where a piece of tissue, usually skin, muscle, or bone, is transferred from one part of the body to another to repair a defect or injury. The tissue is detached from its original blood supply and reattached to a new location using microsurgery techniques. Free flaps can be used to repair a range of conditions, including burns, trauma injuries, and congenital deformities. The most common types of free flaps are skin flaps, muscle flaps, and osteocutaneous flaps. Successful reattachment of the flap relies on precise technique and requires careful monitoring to ensure blood flow is restored.
f. Revascularization procedures
Revascularization procedures are surgical interventions aimed at improving blood flow to the skin and underlying tissues. These procedures involve reconnecting or reconstructing damaged or blocked blood vessels to restore proper circulation. In aesthetic surgery, revascularization is often performed to salvage compromised tissue due to previous surgical trauma, radiation therapy, or congenital conditions. The goal is to improve the appearance of the affected area by reducing discoloration, swelling, and tissue thinning. Revascularization procedures can be performed using various techniques, including microsurgery, flap reconstruction, and tissue transplantation. These procedures can help to restore the natural appearance and function of the affected area.
g. Replantation surgeries
Replantation surgery is a complex procedure that involves reattaching a severed body part, such as a limb, digit, or other tissue, back to the body. The goal is to restore function, sensation, and appearance. The process involves carefully cleaning and preparing the severed part, reattaching it to the remaining tissues, and re-establishing blood flow and nerve connections. Replantation surgery requires a high level of expertise and often involves multiple surgeries. Success rates vary depending on the severity of the injury, the quality of care, and the individual's overall health. Despite the challenges, replantation surgery can lead to remarkable functional and cosmetic outcomes.


